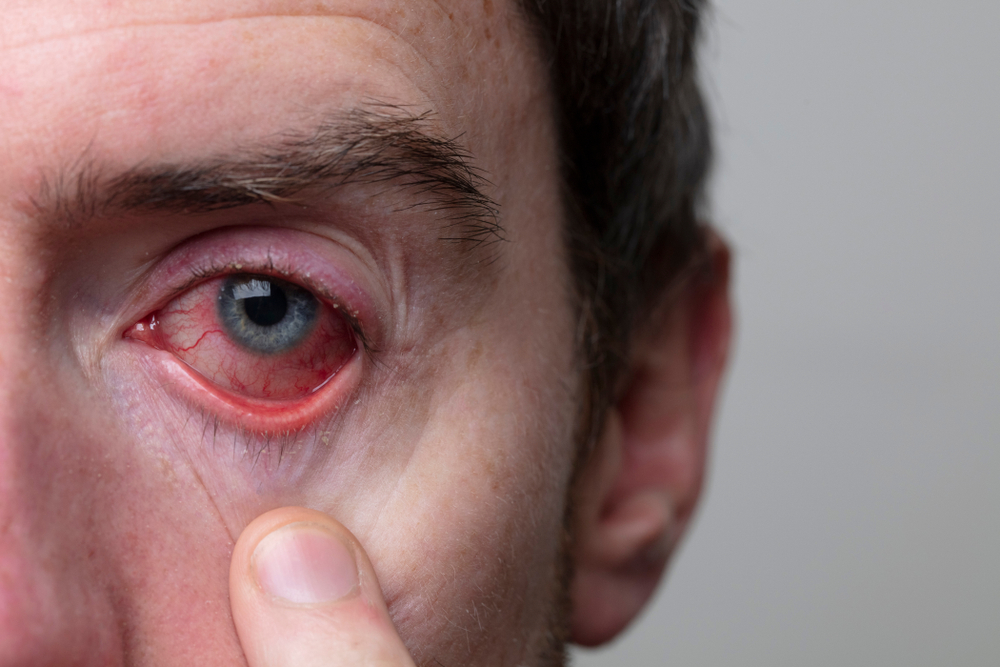
Eye health is critical to our overall well-being, but sometimes, underlying conditions can cause discomfort and even threaten our vision. Uveitis is one such condition—a form of eye inflammation that requires prompt attention and treatment.
What Is Uveitis?
Uveitis refers to inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye that includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. The uvea plays an essential role in supplying blood to the retina and other parts of the eye. When this area becomes inflamed, it can affect vision and, if untreated, lead to complications such as glaucoma, cataracts, or even vision loss.
Uveitis can be classified into different types based on which part of the uvea is inflamed:
Anterior uveitis: Inflammation of the iris and ciliary body (most common type).
Intermediate uveitis: Inflammation in the vitreous humor.
Posterior uveitis: Inflammation of the retina or choroid.
Panuveitis: Inflammation affecting all layers of the uvea.
What Causes Uveitis?
Uveitis can arise from a variety of factors, including:
Autoimmune disorders: Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or ankylosing spondylitis can trigger uveitis.
Infections: Viral, bacterial, or fungal infections such as herpes, syphilis, tuberculosis, or Lyme disease can lead to inflammation.
Trauma: Eye injuries may cause uveitis as a secondary complication.
Unknown causes: In some cases, the specific cause of uveitis cannot be determined, making it idiopathic.
Common Symptoms of Uveitis
The symptoms of uveitis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common signs include:
Redness in the eye
Eye pain or discomfort
Light sensitivity (photophobia)
Blurred or decreased vision
Dark floating spots (floaters)
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek professional care as soon as possible.
How is Uveitis Treated?
Treating uveitis involves addressing its underlying cause and severity, with the primary goals of reducing inflammation, controlling pain, and preserving vision. Various treatment approaches are available depending on the specific circumstances of the condition.
Topical steroids are often the first line of treatment for anterior uveitis. Anti-inflammatory eye drops containing corticosteroids like Prednisone can effectively reduce inflammation in mild cases. For more severe or widespread inflammation, systemic steroids may be prescribed. These can be administered orally or intravenously to manage more advanced cases of uveitis.
When uveitis is linked to an autoimmune disorder or does not respond to steroids alone, immunosuppressant drugs may be necessary. Medications like Methotrexate, Enbrel, Humira, Remicade, and Cellcept help control the overactivity of the immune system and reduce inflammation.
If the uveitis is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics are essential. Specific antibiotics are chosen based on the infection type, such as Doxycycline or Azithromycin for Lyme disease, Rifampin for tuberculosis-related uveitis, or Penicillin for syphilis.
Why Early Detection Matters
Uveitis is a potentially serious condition that can lead to permanent damage if left untreated. Regular eye exams are essential for early detection, especially if you have a history of autoimmune conditions or previous episodes of uveitis. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment can significantly improve outcomes and protect your vision.
Protect Your Vision at The Center for Eye Care
Uveitis is a serious eye condition that requires prompt attention to protect your vision and overall eye health. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments, you can take proactive steps toward managing this condition effectively.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of uveitis, schedule a consultation with The Center for Eye Care for comprehensive care tailored to your needs. Visit our office in West Islip, New York, or call (631) 825-7725 to book an appointment today.










